Deployment Architecture¶
Creating a NebulaGraph service cluster using the CloudFormation template allows you to customize cluster components as needed. This topic describes the recommended deployment architecture for a production environment.
A typical cluster architecture in a production environment is shown in the following figure.
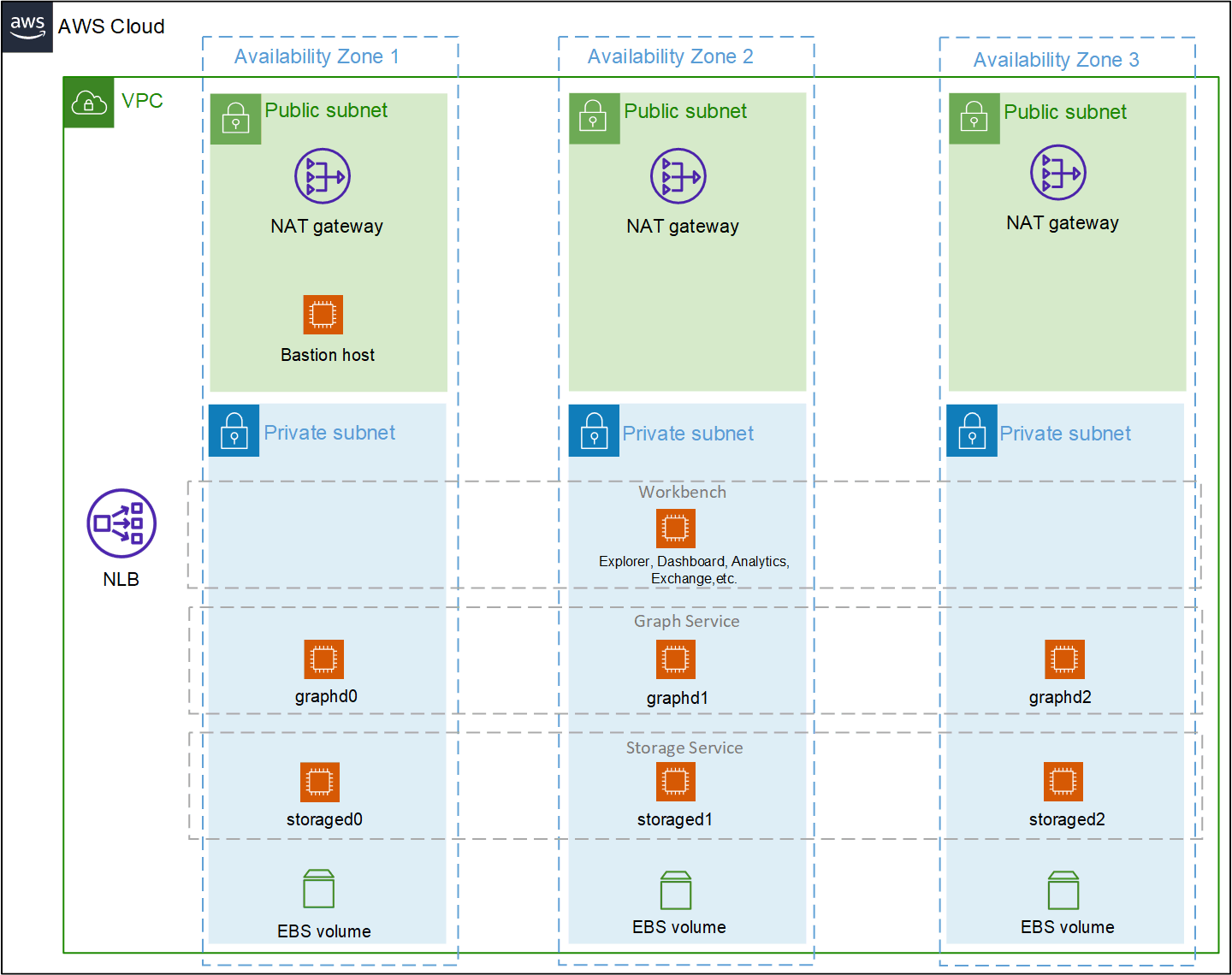
The preceding architecture sets up the following:
- A highly available architecture that spans three Availability Zones.*
- A virtual private cloud (VPC) configured with public and private subnets.*
- A Network Load Balancer for balancing incoming traffic across multiple hosts.*
In the public subnets:
- Managed network address translation (NAT) gateways to allow outbound internet access for resources in the private subnets.*
- A Linux bastion host to allow inbound Secure Shell (SSH) access to Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances in public and private subnets.*
- A NebulaGraph Explorer server for visualized exploration of NebulaGraph data.
In the private subnets:
- A Linux workbench host, where NebulaGraph ecosystem tools such as Explorer, Dashboard, Analytics, and Exchange are deployed together.
- NebulaGraph Graph Service supported by graphd processes. Each graphd process runs in one subnet.
- NebulaGraph Storage Service supported by storaged processes. Each storaged process runs in one subnet.
- An Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume in each subnet.*
Note
The template that deploys NebulaGraph into an existing VPC skips the components marked by asterisks and prompts you for your existing VPC configuration.
Last update:
December 14, 2022