Meta Service¶
This topic introduces the architecture and functions of the Meta Service.
The architecture of the Meta Service¶
The architecture of the Meta Service is as follows:
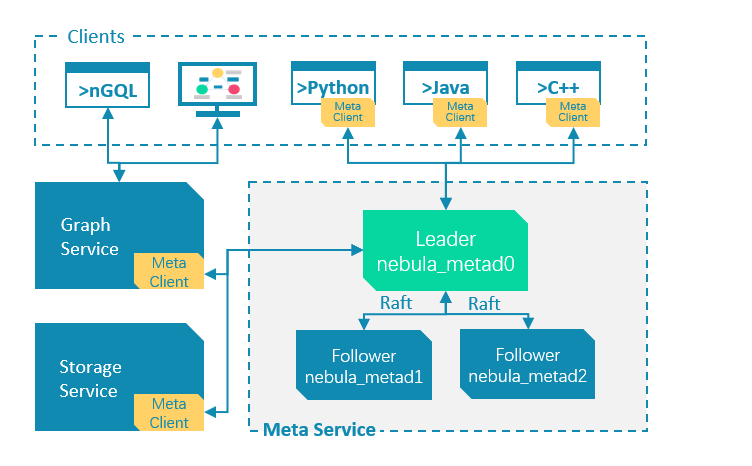
The Meta Service is run by nebula-metad processes. Users can deploy nebula-metad processes according to the scenario:
- In a test environment, users can deploy one or three nebula-metad processes on different machines or a single machine.
- In a production environment, we recommend that users deploy three nebula-metad processes on different machines for high availability.
All the nebula-metad processes form a Raft-based cluster, with one process as the leader and the others as the followers.
The leader is elected by the majorities and only the leader can provide service to the clients or other components of NebulaGraph. The followers will be run in a standby way and each has a data replication of the leader. Once the leader fails, one of the followers will be elected as the new leader.
Note
The data of the leader and the followers will keep consistent through Raft. Thus the breakdown and election of the leader will not cause data inconsistency. For more information on Raft, see Storage service architecture.
Functions of the Meta Service¶
Manages user accounts¶
The Meta Service stores the information of user accounts and the privileges granted to the accounts. When the clients send queries to the Meta Service through an account, the Meta Service checks the account information and whether the account has the right privileges to execute the queries or not.
For more information on NebulaGraph access control, see Authentication.
Manages partitions¶
The Meta Service stores and manages the locations of the storage partitions and helps balance the partitions.
Manages graph spaces¶
NebulaGraph supports multiple graph spaces. Data stored in different graph spaces are securely isolated. The Meta Service stores the metadata of all graph spaces and tracks the changes of them, such as adding or dropping a graph space.
Manages schema information¶
NebulaGraph is a strong-typed graph database. Its schema contains tags (i.e., the vertex types), edge types, tag properties, and edge type properties.
The Meta Service stores the schema information. Besides, it performs the addition, modification, and deletion of the schema, and logs the versions of them.
For more information on NebulaGraph schema, see Data model.
Manages TTL information¶
The Meta Service stores the definition of TTL (Time to Live) options which are used to control data expiration. The Storage Service takes care of the expiring and evicting processes. For more information, see TTL.
Manages jobs¶
The Job Management module in the Meta Service is responsible for the creation, queuing, querying, and deletion of jobs.