Architecture overview¶
NebulaGraph consists of three services: the Graph Service, the Storage Service, and the Meta Service. It applies the separation of storage and computing architecture.
Each service has its executable binaries and processes launched from the binaries. Users can deploy a NebulaGraph cluster on a single machine or multiple machines using these binaries.
The following figure shows the architecture of a typical NebulaGraph cluster.
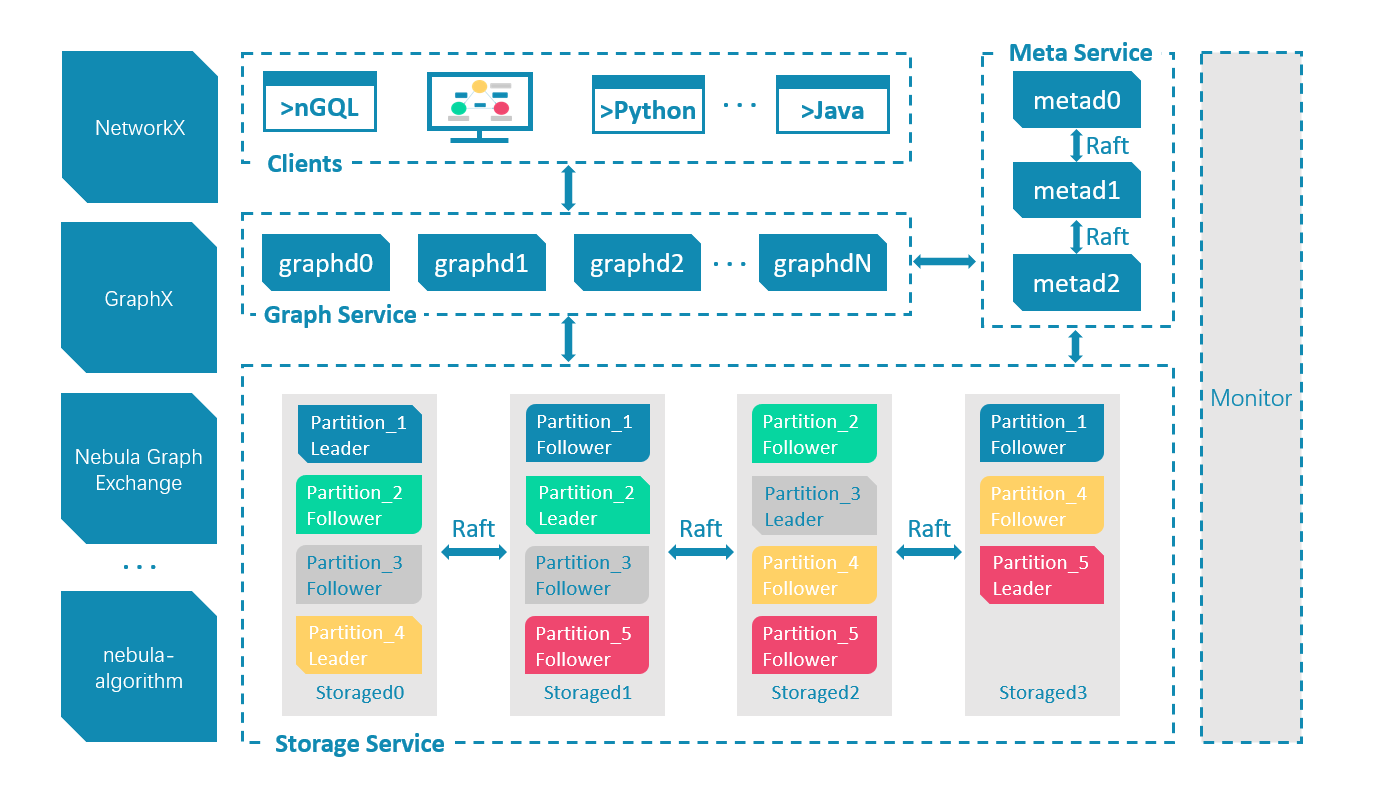
The Meta Service¶
The Meta Service in the NebulaGraph architecture is run by the nebula-metad processes. It is responsible for metadata management, such as schema operations, cluster administration, and user privilege management.
For details on the Meta Service, see Meta Service.
The Graph Service and the Storage Service¶
NebulaGraph applies the separation of storage and computing architecture. The Graph Service is responsible for querying. The Storage Service is responsible for storage. They are run by different processes, i.e., nebula-graphd and nebula-storaged. The benefits of the separation of storage and computing architecture are as follows:
- Great scalability
The separated structure makes both the Graph Service and the Storage Service flexible and easy to scale in or out.
- High availability
If part of the Graph Service fails, the data stored by the Storage Service suffers no loss. And if the rest part of the Graph Service is still able to serve the clients, service recovery can be performed quickly, even unfelt by the users.
- Cost-effective
The separation of storage and computing architecture provides a higher resource utilization rate, and it enables clients to manage the cost flexibly according to business demands.
- Open to more possibilities
With the ability to run separately, the Graph Service may work with multiple types of storage engines, and the Storage Service may also serve more types of computing engines.
For details on the Graph Service and the Storage Service, see Graph Service and Storage Service.