What is Backup & Restore¶
Backup & Restore (BR in short) is a Command-Line Interface (CLI) tool for you to back up data of graph spaces of Nebula Graph and to restore data from the backup files.
Features¶
- Supports storing backup files in local disks (SSD or HDD), Alibaba Cloud OSS, and Amazon S3.
- Supports backing up data of one or multiple graph spaces.
Limitations¶
- Supports Nebula Graph v2.0.0-RC and later versions only.
- Supports full backup, but not incremental backup.
- Supports restoration of data on clusters of the same topologies only, which means both clusters must have exactly the same number of hosts.
- SSH login is required for backup and restoration.
- Does not support the Nebula Graph services deployed with Docker Compose.
- During the backup process, both DDL and DML statements in the specified graph spaces are blocked. We recommend that you do the operation within the low peak period of the business, for example, from 2:00 AM to 5:00 AM.
- The restoration process is performed OFFLINE.
Implementation¶
You can use the BR to do these:
- Backing up a cluster and storing its data in a local or cloud storage system.
- Restoring data to a cluster from a local or cloud storage system.
This section introduces how backup and restoration are implemented in the BR.
Backup¶
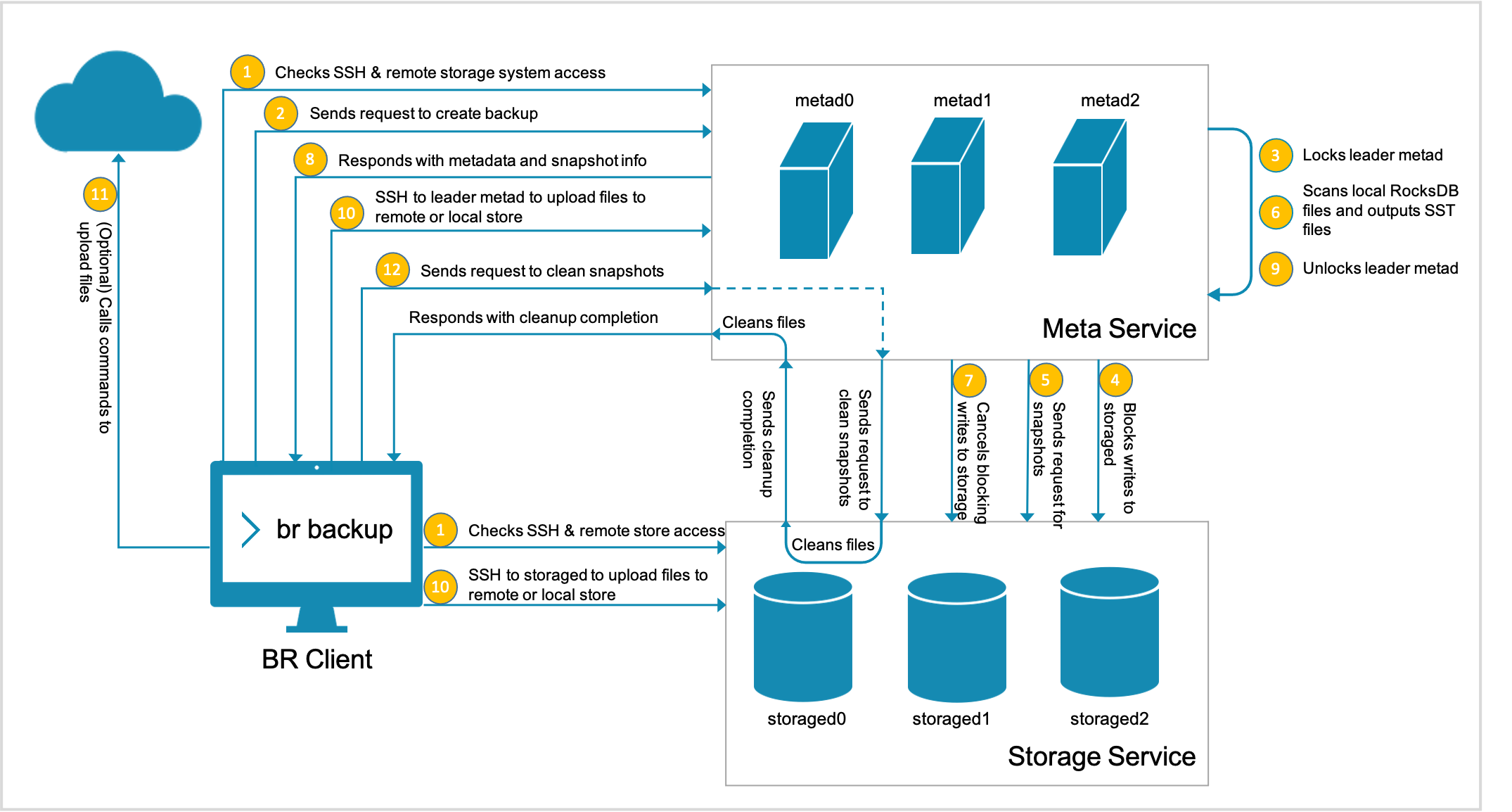
To back up data, the BR sends a backup request to the leader metad process to trigger the backup process as follows:
-
The SSH login from the BR machine to the meta and the storage servers is verified. Besides, if a remote storage system such as Amazon S3 or Alibaba Cloud OSS is necessary, their client installation and configuration are verified.
-
The BR sends a request to create backup files.
-
The leader metad process is locked.
Note
From now on, you cannot run any DDL statement of nGQL until Step 9.
-
The leader metad process blocks writing to the specified graph spaces.
Note
From now on, you cannot run any DML statement of nGQL in the specified graph spaces until Step 7. But this process has no effect on the DQL statements in these graph spaces, and you can do whatever you want in other graph spaces.
-
The leader metad process sends a request to the storaged processes for the snapshot file names.
-
The leader metad process scans local RocksDB files and output SST files.
-
The leader metad process cancels blocking writing to the specified graph spaces.
Note
From now on, you can run DML statements in the specified graph spaces.
-
The leader metad process sends responses to the BR with the metadata including:
- the thrift format, partition information of the graph spaces, and the Raft log commit ID of each partition, and
- the snapshot information including the catalog of the snapshots of each storaged process, their SST file names of the meta server, and the backup file names.
-
The leader metad process is unlocked.
Note
From now on, you can run any DDL statement in the specified graph spaces.
-
The account on the BR machine logs on via SSH to the meta server where the leader locates and to all the storage servers, and backs up files.
-
If Amazon S3 or Alibaba Cloud OSS is used, the BR calls commands to upload the files to the cloud storage system.
Note
This step causes massive disk reads. We recommend that a 10 Gigabit Network is applied. If a networking error occurs during this step, the backup process fails and you must do the backup operation again. For now, the backup process cannot be resumed from the broken point.
-
The BR sends a request to clean the snapshots from meta server and storage servers, and the backup process is done.
This figure shows how the backup is implemented.
When backup files are generated, the file names are generated automatically. A folder name is in the format of BACKUP_YY_MM_DD_HH_mm_SS, of which,
BACKUPindicates the files are backup files.YY_MM_DD_HH_mm_SSindicates the timestamp when the files are generated.
Restore¶
Caution
During the restoration process, the data on the target cluster is removed and then is replaced with the data from the backup files. If necessary, back up the data on the target cluster.
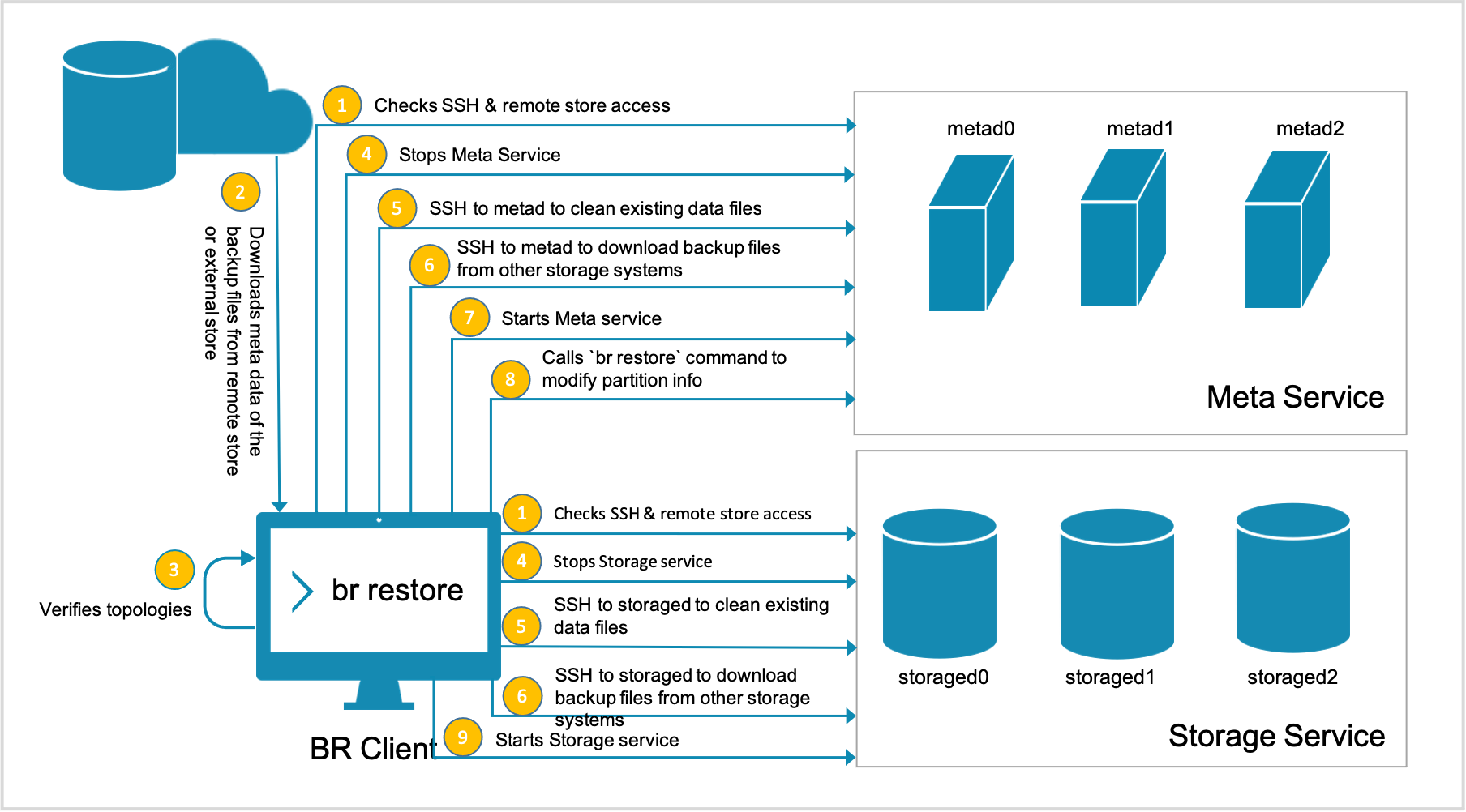
The restoration process is implemented as follows:
-
The SSH login from the BR to the meta and the storage servers is verified. Besides, if a cloud storage system such as Amazon S3 or Alibaba Cloud OSS is necessary, their client installation and configuration are verified.
-
The BR downloads the metadata (but not data) of the backup files from the remote storage system or other external storage systems.
-
The BR verifies the topology of the clusters.
-
The BR stops the Meta Service and the Storage Service remotely.
-
The account on the BR machine logs on via SSH to the meta and storage servers to remove the existing data files.
-
When data files are removed, the account on the BR machine logs on via SSH to the meta and storage servers and downloads the backup files from the cloud storage system or other external storage systems.
-
When the backup files are downloaded, the BR starts the Meta Service.
-
The BR calls the
br restorecommand to change the partition information of the specified metad processes. -
The BR starts the Storage Service, and the restoration process is done.
This figure shows how the restoration process is implemented.
How to use¶
To use the BR, follow these steps: